Geothermal heat pumps are an innovative and sustainable technology that harnesses the Earth’s natural heat to provide efficient heating, cooling, and even hot water for residential and commercial spaces. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into what geothermal heat pumps are, how they work, and the different types of systems available.
What Is a Geothermal Heat Pump?
A geothermal heat pump, also known as a ground source heat pump, is a heating and cooling system that utilizes the constant temperature of the Earth to exchange heat with a building. Unlike traditional HVAC systems that rely on external air, Ground-source heat pumps tap into the Earth’s stable temperature to provide energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
How Does a Geothermal Heat Pump Work?
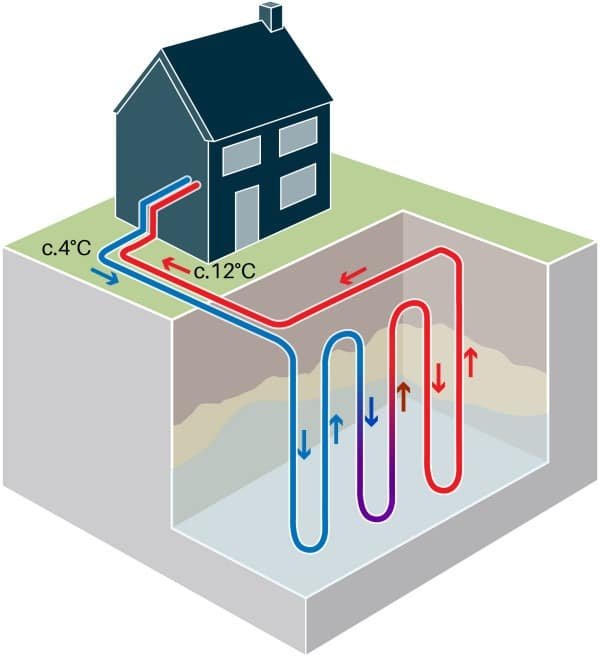
Geothermal heat pumps work on the principle of transferring heat between a building and the Earth. The system consists of a heat pump unit, a ground heat exchanger, and a distribution system. The ground heat exchanger is a loop of pipes buried underground, containing a fluid that absorbs or releases heat as it circulates. The heat pump then amplifies and distributes this heat to provide comfortable temperatures inside the building.
Types of Geothermal Heat Pump Systems

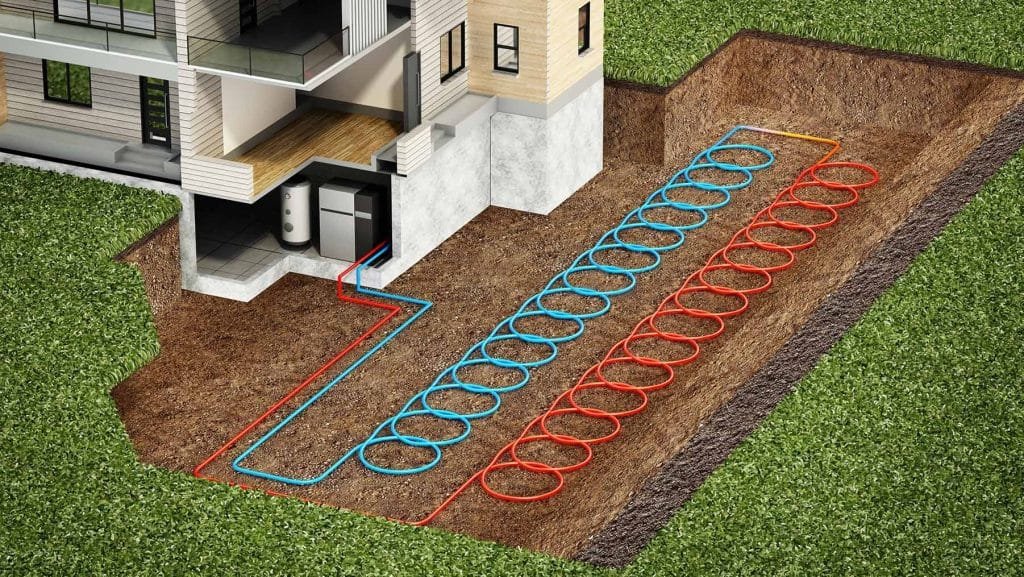
Horizontal System:
The horizontal geothermal heat pump system involves burying pipes in trenches horizontally across a wide area. This type is suitable for properties with ample land space. The pipes absorb heat from the ground in the winter and release heat to the ground in the summer, providing efficient year-round temperature control.
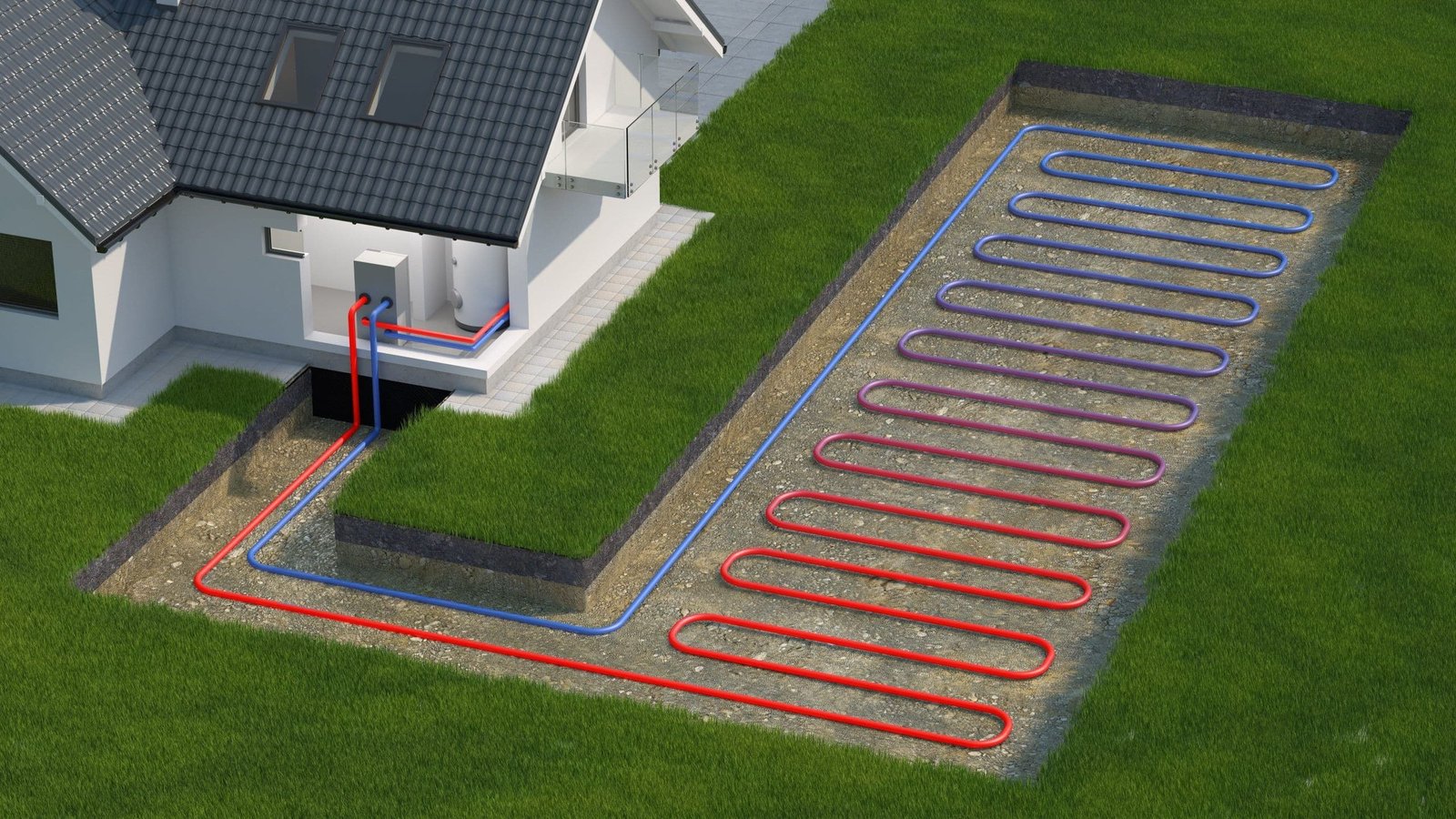
Vertical System:
Vertical geothermal heat pump systems are ideal for properties with limited space. In this setup, pipes are drilled vertically into the ground, allowing for effective heat exchange without requiring extensive land. Vertical systems are versatile and can be installed in a variety of locations, making them a popular choice for urban environments.
Pond/Lake System:

Pond or lake geothermal pump systems utilize bodies of water for heat exchange. Pipes are submerged in the water, absorbing or releasing heat as needed. This system is particularly advantageous in areas with accessible water sources, offering an energy-efficient solution with minimal environmental impact.
Environmental Benefits of Geothermal Heat Pumps:
Geothermal heat pumps are renowned for their environmental friendliness. Unlike traditional heating and cooling systems that rely on fossil fuels, geothermal systems generate minimal greenhouse gas emissions. They use the Earth’s renewable energy, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources and contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
What Are the Downsides of a Geothermal Heat Pump?
While Subsurface heat pumps offer numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge some downsides associated with their installation and use. Firstly, the initial installation cost can be higher than traditional heating and cooling systems, primarily due to the need for drilling or extensive excavation. Site-specific challenges, such as limited space or unsuitable soil conditions, may also affect installation feasibility.
Additionally, the efficiency of geothermal systems relies heavily on the heat transfer capabilities of the ground. In some regions, the temperature gradient may not be sufficient to meet the heating or cooling demands of the building, potentially impacting overall system efficiency. Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance, and repairs to the underground piping can be more complex and costly than those for traditional HVAC systems.
Despite these challenges, many homeowners and businesses find that the long-term benefits, such as energy savings and environmental sustainability, outweigh the initial drawbacks. Careful consideration of site conditions and thorough planning can help mitigate these downsides, ensuring a successful and efficient geothermal pump system.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Savings:
While the initial installation cost of a geothermal heat pump system may be higher than traditional systems, the long-term savings are substantial. Geothermal systems have lower operating costs, reduced maintenance requirements, and longer lifespans, making them a cost-effective investment in the long run.
Government Incentives and Rebates:
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, including Soil-sourced heat pumps. Homeowners and businesses may be eligible for tax credits, rebates, or other financial incentives, making the transition to geothermal heating and cooling more economically viable.
Maintenance and Lifespan:
Geothermal heat pumps are known for their low maintenance requirements and extended lifespan. With proper care, these systems can last for several decades. Regular inspections and maintenance, typically performed by certified technicians, ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency in Extreme Climates:
Geo-exchange systems excel in extreme climates, providing consistent heating in the winter and cooling in the summer. Unlike air-source heat pumps that may struggle in extremely cold conditions, geothermal systems maintain their efficiency by tapping into the stable temperatures below the Earth’s surface.
Zone Heating and Cooling:
Geothermal heat pump systems can be designed for zone heating and cooling, allowing for personalized temperature control in different areas of a building. This zoning capability enhances comfort and energy efficiency by directing heating or cooling where it is needed, reducing energy consumption in unused spaces.
Minimal Noise Pollution:
Compared to traditional HVAC systems, pumps operate quietly. The absence of noisy outdoor condenser units contributes to a more peaceful and comfortable living or working environment. This makes geothermal systems particularly attractive for residential areas or commercial spaces where noise pollution is a concern.
Reducing Carbon Footprint:
Heat pumps significantly reduce carbon footprints, as they rely on a renewable and constant energy source. By decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, these systems help combat climate change and contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet. Choosing geothermal technology aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to sustainable energy solutions.
Adaptability to Existing Buildings:
Geothermal heat pump systems can often be retrofitted to existing buildings, offering a sustainable upgrade for older structures. While ideal for new constructions, the adaptability of geothermal systems makes them a feasible option for those looking to enhance the energy efficiency of their current heating and cooling setups.
Enhanced Property Value:
Investing in a geothermal heat pump system can enhance the overall value of a property. As energy efficiency becomes a priority for homebuyers and businesses alike, having a geothermal system in place can make a property more attractive, potentially increasing its resale value.
Technological Advancements:
Ongoing advancements in geothermal heat pump technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Innovations in materials, design, and installation techniques contribute to the evolution of these systems, making them even more accessible and effective for a broader range of applications.
Community and Environmental Impact:
The adoption of heat pump technology can have positive effects on local communities and the environment. By reducing the demand for conventional heating and cooling methods, geothermal systems contribute to cleaner air and water, helping create more sustainable and resilient communities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What types of geothermal heat pump systems are available?
Ans: There are three main types: horizontal systems, which use trenches for piping; vertical systems, where pipes are drilled vertically into the ground; and pond/lake systems, utilizing water bodies for heat exchange.
Are geothermal heat pumps suitable for all climates?
Ans: Geothermal heat pumps work well in various climates, but their efficiency can be affected by extreme temperature conditions. They are particularly effective in moderate climates and can still be efficient in colder climates with proper design and installation.
How long does a geothermal heat pump system last?
Ans: With proper maintenance, geothermal heat pump systems can last for more than 20 years. The underground components often have a longer lifespan than traditional HVAC systems.
How noisy are geothermal heat pump systems?
Ans: This pump systems operate quietly, especially when compared to traditional HVAC systems. The absence of noisy outdoor condenser units contributes to a quieter living or working environment.
What maintenance is required for a geothermal heat pump system?
Ans: Regular maintenance, including inspections and checks on the fluid levels and system components, is essential for optimal performance. While geothermal systems generally have lower maintenance requirements than traditional systems, professional servicing is recommended to ensure longevity and efficiency.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, geothermal heat pumps offer a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. Understanding how these systems work and the various types available allows consumers to make informed decisions for their homes or businesses. With environmental benefits, cost efficiency, and long-term savings, This heat pumps present a promising solution for a more sustainable and comfortable future.
Read more article! visit here